Deployment / ReplicaSet

Useful Links
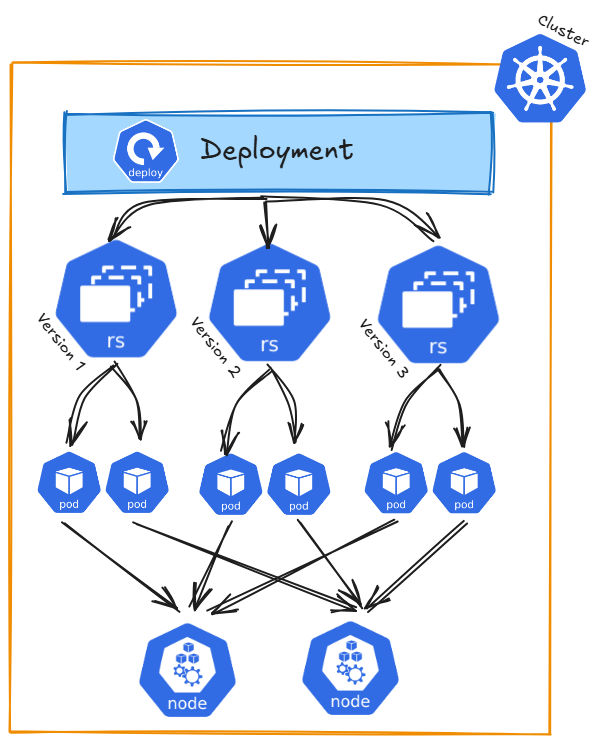
Architecture
Detailed Description
Kubernetes Deployments serve as a blueprint for running your application in a cluster. Building on ReplicaSets, they ensure your application remains in the desired state by maintaining the defined number of instances.
ReplicaSets take care of the following:
- Ensuring the desired number of Pods are always running
- Replacing failed Pods automatically to maintain the specified replicas
On top of that, a Deployment adds powerful features, such as:
- Automatically rolling out new versions of your application
- Rolling back to a previous version if something goes wrong
- Managing updates with strategies like rolling updates or recreating Pods
Command Reference Guide
Remeber to use dry-run and tee to check the configuration of each command first.
--dry-run=client -o yaml | tee nginx-deployment.yaml
Create a ReplicaSet using a YAML file (declarative method)
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: nginx-replicaset
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginxdemos/hello
ports:
- containerPort: 80
# Apply replicaset
kubectl apply -f nginx-replicaset.yaml
# Get ReplicaSet informatoin
kubectl get replicaset nginx-replicaset -o wide
# Get detailed ReplicaSet information
kubectl describe replicaset/nginx-replicaset
# Check the current Pods running
kubectl get pods
# Delete a Pod of the ReplicaSet
FIRST_POD=$(kubectl get pods -l app=nginx -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
kubectl delete pod $FIRST_POD
# Recheck running Pods
kubectl get pods
# Change image in yaml to nginxdemos/hello:v0.2 and apply replicaset again
kubectl apply -f nginx-replicaset.yaml
# You will encounter that the replicaset was updated - but the pods are still using the old image
kubectl describe replicaset/nginx-replicaset
kubectl describe pod/<podname>
# You have to kill and recreate the pods, so the new ones will be created with the new image. (see Hint section)
FIRST_POD=$(kubectl get pods -l app=nginx -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
kubectl scale rs nginx-replicaset --replicas=0
kubectl scale rs nginx-replicaset --replicas=3
kubectl describe pod/$FIRST_POD
Create a Deplyoment (imperative method)
# Create nginx deployment with the default of one replica
kubectl create deployment nginx-deployment --image=nginxdemos/hello --port=80
# Create nginx deployment with three replicas
kubectl create deployment nginx-deployment --image=nginxdemos/hello --port=80 --replicas=3
# Check deployment
kubectl get deployment -o wide
# Get detailed deployment information
kubectl describe deployment
# Get ReplicaSet information created by deployment
kubectl get replicasets -o wide
# Get History for deployment
kubectl rollout history deployment/nginx-deployment
# Annotate inital history entry
kubectl annotate deployment/nginx-deployment kubernetes.io/change-cause="init nginx deployment"
kubectl rollout history deployment/nginx-deployment
# Scale up/down deployment (scale is not changing history)
kubectl scale deployment/nginx-deployment --replicas=5; watch kubectl get pods -o wide
kubectl scale deployment/nginx-deployment --replicas=3; watch kubectl get pods -o wide
# Delete deployment
kubectl delete deployment/nginx-deployment
Hints
Deployments manage ReplicaSets, primarily due to historical reasons. There is no practical need to manually create ReplicaSets (or previously, ReplicationControllers), as Deployments, built on top of ReplicaSets, offer a more user-friendly and feature-rich abstraction for managing the application lifecycle, including replication, updates, and rollbacks.
ReplicaSets do not support auto updates. As long as required number of pods exist matching the selector labels, replicaset's jobs is done.
Open questions
./.
My personal summary
./.